NSISArray Script Header Documentation
1.0 Script header documentation contents
- 1.1 Introduction
- 1.2 Include the script header
- 1.3 Creating an array
- 1.4 Initialising an array for run-time use
- 1.5 Declaring array functions
- 1.6 Array functions
- 1.6.1 ${myArray->Write}
- 1.6.2 ${myArray->WriteList}
- 1.6.3 ${myArray->WriteListC}
- 1.6.4 ${myArray->Put}
- 1.6.5 ${myArray->Read}
- 1.6.6 ${myArray->ReadToStack}
- 1.6.7 ${myArray->Cut}
- 1.6.8 ${myArray->Push}
- 1.6.9 ${myArray->Pop}
- 1.6.10 ${myArray->Shift}
- 1.6.11 ${myArray->Unshift}
- 1.6.12 ${myArray->Reverse}
- 1.6.13 ${myArray->Sort}
- 1.6.14 ${myArray->SortNumeric}
- 1.6.15 ${myArray->Clear}
- 1.6.16 ${myArray->Splice}
- 1.6.17 ${myArray->Swap}
- 1.6.18 ${myArray->Copy}
- 1.6.19 ${myArray->Join}
- 1.6.20 ${myArray->Concat}
- 1.6.21 ${myArray->Exists} & ${myArray->ExistsI}
- 1.6.22 ${myArray->Search} & ${myArray->SearchI}
- 1.6.23 ${myArray->SizeOf}
- 1.6.24 ${myArray->SetSize}
- 1.6.25 ${myArray->ReadFirst}, ${myArray->ReadNext} & ${myArray->ReadClose}
- 1.6.26 ${myArray->ReDim}
- 1.6.27 ${myArray->FreeUnusedMem}
- 1.6.28 ${myArray->Subtract}
- 1.6.29 ${myArray->SetAutoRedim}
- 1.7 Deleting an array object
- 1.8 Array auto-redimensioning
- 1.9 Array debugging
- 1.10 Examples
- 1.11 Jumping over NSISArray functions
- 1.12 Calculating memory usage
1.1 Introduction
The NSISArray script header is a macro system for the NSISArray plug-in by Afrow UK.
The NSISArray script header masks the plug-in calls with a more friendly scripting language syntax. Everything else is managed on the plug-in side.
Information about the NSISArray plug-in is under the NSISArray Plug-in Documentation section.
Before you write any code, you might want to read section 1.11 Jumping over NSISArray instructions.
1.1.1 What is an array?
Arrays allow you to hold masses of data under a single 'object'.
Arrays are very useful when we'd like to store an unknown amount of data. With NSISArray the arrays expand in size when more data is added.
1.1.2 NSISArray vs Afrow UK's Array.nsh script header
The first array script header by Afrow UK uses INI files to store the data. It has many of the same functions, but all of the code is written in NSIS and reading and writing to text files makes it much much slower.
The original array script header is still available here; http://nsis.sf.net/wiki/File:Array.zip, although development and support has discontinued.
1.2 Include the script header
The plugin DLL file (NSISArray.dll) should be placed in the NSIS plugins folder (usually C:\Program Files\NSIS\Plugins).
The plugin NSH file (NSISArray.nsh) should be placed in the NSIS include folder (usually C:\Program Files\NSIS\Include).
Place !include NSISArray.nsh at the top of your script to start using the script header.
Any array instructions and special settings must be used afterwards and not before.
1.2.1 Special settings
Some optional special settings can be !defined before the first ${Array} instruction. These include:
1.2.1.1 !define ArrayPlugin [plugin_name]
Specifies that the script header should use the [plugin_name] plug-in file name (do not include '.dll'). By default, the script header uses "NSISArray".
1.2.1.2 !define ArrayCallInstDLL [dll_path]
Specifies that the script header should call the plug-in with CallInstDLL, and call a DLL file at [dll_path].
Note: [dll_path] is the full path to the NSISArray plug-in DLL file at run time. This could be for example, "$EXEDIR\dllcache\Arrays.dll".
Please also note that the ${myArray->WriteList} and ${myArray->Splice} functions change when using this special setting.
This setting overrides the ArrayPlugin special settings.
1.2.1.3 !define ArrayValVar $Var
Specifies the variable to use within the script header macros for certain purposes. If not defined, the variable $ArrayVal will be declared.
1.2.1.4 !define ArrayErrVar $Var
Specifies the variable to use for error reporting. If not defined, the variable $ArrayErr will be declared.
The $ArrayErr variable will contain the error code when a array function fails. See section 1.9.1.2 Checking the $ArrayErr variable for more information.
1.2.1.5 !define ArraySetErrors
This causes the NSISArray script header to set the NSIS error flag when a call to a plug-in function fails. For more information, see section 1.9.1.3 Checking for errors with the NSIS IfErrors function.
1.3 Creating an array
To create an array, use:
${Array} myArray [x] [y]
Where myArray is any custom name for an array object.
This function must be used outside Sections and Functions, preferably near the top of your script (but after !include NSISArray.nsh).
The [x] and [y] parameters specify the initial array dimensions. [x] being the number of empty indices initially allocated to the array and [y] being the initial buffer length of all the array's items.
Both the array's number of allocated indices and buffer lengths can be changed manually at run time with the ${myArray->ReDim} function.
The minimum value of [x] can be 1 and the minimum value of [y] can be 2.
Please note that the value for buffer lengths ([y]) must always allow for the NULL escaping character on the end of strings to prevent buffer overflows. For example, if you're only putting single characters in the array, the [y] value must be 2 and not 1.
1.3.1 Changing the object delimiter
By default, the array delimiter used for object functions is ->. This can be changed using:
${ArrayObj} [new_delimiter]
The [new_delimiter] parameter specifies the delimiter to use, which could be any character or characters of your choice. Some of the script examples under the Examples folder use a dot (.).
This function can only be used just after array creation with the ${Array} function and applies to that array object only. It also cannot be used after using the ${ArrayFunc} function.
1.4 Initialising an array for run-time use
Even after declaring an array with ${Array}, the array still needs to be initialised for use at run-time. This could be in Function .onInit or perhaps just before using the array in a Section.
To initialise an array use:
${myArray->Init}
You must always initialise an array before use.
Note: This is necessarily just before you use the array in your NSIS script, but before the array is used at run-time.
There are error messages specific to the NSISArray script header for this function which are listen under section 1.9.3 NSIS compiler errors.
1.4.1 Check if an array has already been initialised
To check if an array has been initialised, use:
${myArray->Inited} [jump_if_initialised] [jump_if_not_initialised]
Both [jump_if_initialised] and [jump_if_not_initialised] can be relative jumps, e.g. +2 or label jumps.
Note: As the NSISArray script header is macro based, the two parameters are not optional. Use 0 or "" for either parameter for a non jump.
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\Inited.nsi.
1.5 Declaring array functions
To use any of the array functions available, you must declare them at the top of your script first with the ${ArrayFunc} function:
${Array} myArray1
${ArrayFunc} Read
${ArrayFunc} Write
${ArrayFunc} Splice
${Array} myArray2
${ArrayFunc} Cut
${ArrayFunc} Debug
etc...
With the above example the Read, Write and Splice functions will be declared for myArray1; and the Cut and Debug functions will be declared for myArray2.
Failure to declare a function for an individual array will result in the compile error:
'Invalid command: ${myArray->FuncName}'
Please note that you do not need to declare the Init and Delete array functions as they are not optional.
1.6 Array functions
NSISArray comes with plenty of functions for managing your arrays.
Please note that much like in many programming languages, we refer to array items with an index number. This index number is also zero base, which means the first item in an array will be at index 0 and not 1.
1.6.1 ${myArray->Write} [index] "string"
Writes "string" to [index] in myArray, overwriting any existing items or adding an item if the specified index is one greater than the current highest item index.
${myArray->Write} 0 "A string to save!"
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\Write.nsi.
1.6.2 ${myArray->WriteList} '"string 1" "string 2" "string 3" ... '
Writes a list of strings to myArray. Each separate string in quotes will become a separate array item. Any existing myArray array items that are inside the range of the item list will be overwritten.
${myArray->WriteList} '"One string" "Another string" "One more"'
1.6.2.1 ${myArray->WriteList} & ArrayCallInstDLL
If you're using the ArrayCallInstDLL special setting then you will find that you cannot use the standard ${myArray->WriteList} function. A new format is introduced to deal with passing multiple items to the plug-in.
New format:
${myArray->WriteListBegin}
${myArray->WriteListItem} "string 1"
${myArray->WriteListItem} "string 2"
${myArray->WriteListItem} "string 3"
${myArray->WriteListEnd}
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\WriteList.nsi.
1.6.3 ${myArray->WriteListC} "string 1[char]string 2[char]..." "[char]"
Writes a list of strings to myArray separated by single [char]'s. Each separate string will become a separate array item. Any existing myArray array items that are inside the range of the item list will be overwritten.
Note: [char] must be a single character. A string is not allowed.
${myArray->WriteListC} "One string|Another string|One more" "|"
This is ideal for working with InstallOptions ListBox controls.
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\WriteListC.nsi.
1.6.4 ${myArray->Put} [index] "string"
Puts "string" into myArray at [index]. No existing items are overwritten, but moved up by one.
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\Put.nsi.
1.6.5 ${myArray->Read} $Var [index]
Reads a string from [index] in myArray and places the string into $Var.
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\Read.nsi.
1.6.6 ${myArray->ReadToStack} [index_start] [index_end]
Reads strings from item at [index_start] to [index_end] in myArray and places all strings onto the stack. The strings on the stack can then be looped through via Pop until a specific string is reached.
Note: If [index_end] is a negative number, the end range will be up to the end of the array minus [index_end] inclusive, and so -1 will be up to and including the last item in the array.
Push "stop_popping"
${myArray->ReadToStack} 0 -1
Loop:
Pop $R0
StrCmp $R0 "stop_popping" Done
...do something here...
Goto Loop
Done:
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\ReadToStack.nsi.
1.6.7 ${myArray->Cut} $Var [index]
Cuts a string from myArray at [index]. The string is placed into $Var. Any proceeding array items are moved down by one.
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\Cut.nsi.
1.6.8 ${myArray->Push} "string"
Pushes "string" to the front of myArray.
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\Push.nsi.
1.6.9 ${myArray->Pop} $Var
Pops a string from the front of myArray into $Var.
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\Pop.nsi.
1.6.10 ${myArray->Shift} "string"
Pushes a string to the end of myArray.
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\Shift.nsi.
1.6.11 ${myArray->Unshift} $Var
Pops a string from the end of myArray and places the string into $Var.
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\Unshift.nsi.
1.6.12 ${myArray->Reverse}
Reverses the contents of myArray.
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\Reverse.nsi.
1.6.13 ${myArray->Sort} myArray2
Sorts the contents of myArray alphabetically, also rearranging the contents of myArray2 into the same order.
The myArray2 parameter is optional (it can be left empty "").
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\Sort.nsi, Examples\NSISArray\Sort2Arrays.nsi and Examples\NSISArray\MakeFileList.nsi.
1.6.14 ${myArray->SortNumeric} myArray2
Sorts the contents of myArray numerically, also rearranging the contents of myArray2 into the same order.
The myArray2 parameter is optional (it can be left empty "").
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\SortNumeric.nsi.
1.6.15 ${myArray->Clear}
Clears the contents of myArray. All items are removed and the array size is reset to 0.
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\Clear.nsi.
1.6.16 ${myArray->Splice} [index_start] [index_end] '"string 1" "string 2" ... '
Places a list of strings at [index_start] replacing existing array items up to and including [index_end]. If [index_start] and [index_end] are equal, no existing array items are overwritten.
Specifying no list of strings ('') will result in items from [index_start] up to [index_end] inclusive being deleted.
If [index_end] is a negative number, the end range will be up to the end of the array minus [index_end] inclusive, and so -1 will be up to and including the last item in the array.
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\Splice.nsi.
1.6.17.1 ${myArray->Splice} & ArrayCallInstDLL
If you're using the ArrayCallInstDLL special setting then you will find that you cannot use the standard ${myArray->Splice} function. A new format is introduced to deal with passing multiple items to the plug-in.
New format:
${myArray->SpliceBegin} [index_start] [index_end]
${myArray->SpliceItem} "string 1"
${myArray->SpliceItem} "string 2"
${myArray->SpliceEnd}
The [index_start] and [index_end] parameters are explained under section 1.6.16 ${myArray->Splice} (above).
1.6.17 ${myArray->Swap} [index_1] [index_2]
Swaps the strings in the two indices in myArray.
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\Swap.nsi.
1.6.18 ${myArray->Copy} myArray2
Copies the contents of myArray to myArray2, overwriting any existing items.
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\Copy.nsi.
1.6.19 ${myArray->Join} myArray2
Copies the contents of myArray onto the end of myArray2.
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\Join.nsi.
1.6.20 ${myArray->Concat} $Var [join_char(s)]
Joins all strings in myArray together with [join_char(s)] and places the output in $Var.
${myArray->Join} $R0 " "
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\Concat.nsi.
1.6.21 ${myArray->Exists} $Var "string" [index]
Finds the index of an item that is exactly equal to "string" case sensitively in myArray after [index].
$Var will contain the item index, or -1 if not found.
Note: To search non case sensitively, use ${myArray->ExistsI} (that's a capital i) instead of ${myArray->Exists}.
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\Exists.nsi and Examples\NSISArray\ExistsI.nsi.
1.6.22 ${myArray->Search} $Var "string" [index]
Searches through all items after [index] in myArray for "string" case insensitively.
$Var will contain the item index containing the first match, or -1 if not found.
Note: To search non case sensitively, use ${myArray->SearchI} (that's a capital i) instead of ${myArray->Search}.
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\Search.nsi and Examples\NSISArray\SearchI.nsi.
1.6.23 ${myArray->SizeOf} $Var1 $Var2 $Var3
For myArray, $Var1 will now contain the allocated buffer length for all items in the array.
$Var2 will contain the number of allocated array indices.
$Var3 will contain the number of items (used indices) in the array.
1.6.24 ${myArray->SetSize} [size]
Sets the new size of myArray to [size]. If the array is currently smaller than [size], new empty "" items are added. If the array is currently larger than [size], items are removed until it becomes that size.
Note: This does not allocated more memory for more items to be added. To do so, use ${myArray->ReDim}.
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\SetSize.nsi.
1.6.25 ${myArray->ReadFirst} $Handle $OutVar
${myArray->ReadNext} $Handle $OutVar
${myArray->ReadClose} $Handle
These functions are used to loop through an array, and work in a similar fashion to NSIS's FindFirst, FindNext and FindClose.
${myArray->ReadFirst} opens a loop for myArray using the $Handle variable for the handle. The first read value will be in $Var. The error flag will be set if this command fails (which can be checked with IfErrors.) Always use ClearErrors first!
${myArray->ReadNext} reads the next value in the array using the $Handle handle, where the value will be placed into $Var. This also sets the error flag.
${myArray->ReadClose} simply closes the array reading. This isn't really necessary, but it's there to keep in with the style of the other NSIS commands.
ClearErrors
${myArray->ReadFirst} $R0 $R1
Loop:
IfErrors Done
DetailPrint $R1
ClearErrors
${myArray->ReadNext} $R0 $R1
Goto Loop
Done:
${myArray->ReadClose} $R0
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\ReadFirst.nsi.
1.6.26 ${myArray->ReDim} [x] [y]
Redimensions myArray to [x] item indices and [y] buffer lengths. No existing items will be deleted. If the number of new indices allocated is less than the number of currently allocated indices, the excess indices are deleted. If the new allocated buffer length is less than the currently allocated buffer length, strings of a greater length are truncated.
The minimum value of [x] can be 1 and the minimum value of [y] can be 2.
Please note that the value for buffer lengths ([y]) must always allow for the NULL escaping character on the end of strings to prevent buffer overflows. For example, if you're only putting single characters in the array, the [y] value must be 2 and not 1.
There are error messages specific to the NSISArray script header for this function which are listen under section 1.9.3 NSIS compiler errors.
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\ReDim.nsi.
1.6.27 ${myArray->FreeUnusedMem}
Frees unused memory in myArray by deleting empty item indices and by decreasing the buffer length for all array items to fit the largest string in the array. Ideally you should call this after you've finished writing to the array.
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\FreeUnusedMem.nsi.
1.6.28 ${myArray->Subtract} myArray2
Removes items from myArray that are also in myArray2. Items are matched case sensitively.
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\Subtract.nsi.
1.6.29 ${myArray->SetAutoRedim} [indices] [str_len]
Sets the number of indices and characters to be increased by when the array is to be auto-redimensioned (for extra memory allocation).
If adding lots of items at a time, you should set [indices] to a larger number than default.
For default values (before or without using this function) and more information on array auto-redimensioning, see section 2.7 Array auto-redimensioning.
There are error messages specific to the NSISArray script header for this function which are listen under section 1.9.3 NSIS compiler errors.
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\SetAutoRedim.nsi.
1.7 Deleting an array object
Deleting an array is not optional. You must always delete an array when you have finished using it. If you don't, the memory allocated for use may not be freed when the installer is closed.
When you are ready to delete an array, use:
${myArray->Delete}
Deleting an array will remove it from memory, but you can still reference that array in your NSIS script. If you do, however, an error will be thrown by the NSISArray plug-in at run time.
For a compilable NSIS script example which demonstrates how an array object may still be referenced after calling the Delete instrction, see Examples\NSISArray\Delete.nsi.
1.7.1 Unloading the NSISArray plug-in
Once all arrays have been deleted with the ${myArray->Delete} function, the plug-in will automatically be unloaded, allowing the plug-in to be deleted from the $PLUGINSDIR folder.
1.8 Array auto-redimensioning
From NSISArray v1.1 and upwards, arrays are now fully dynamic in both item indices (the number of elements) and buffer lengths (the length of strings).
For a complete extended description, see section 2.7 Array auto-redimensioning.
1.9 Array debugging
1.9.1 Catching plug-in errors
Sometimes errors can occur when calling a plug-in function. Usually they are caused by passing bad parameter values, but there are also a few other reasons.
There are a few methods to check for errors, which are listed below...
1.9.1.1 Enabling plug-in error messages
The NSISArray plug-in can display error message boxes or display errors in the NSIS InstFiles Page log window when an error occurs, except this feature is disabled by default. See section 1.9.4 Enabling error messages with ${ArrayErrorStyle}.
1.9.1.2 Checking the $ArrayErr variable
When errors occur in plug-in function calls, the $ArrayErr variable will always contain the error code, or 0 if no error occured after a plug-in function call.
You can easily check the value of $ArrayErr with straight through functions such as DetailPrint or MessageBox, or with flow control functions such as StrCmp.
You can also force the NSISArray script header to use a different variable for error codes. See section 1.2.1.4 !define ArrayErrVar $Var.
1.9.1.3 Checking for errors with the NSIS IfErrors function
By default, the NSISArray script header does not set the NSIS error flag (with SetErrors). However, there is a setting to enable this which you'll find under section 1.2.1.5 !define ArraySetErrors.
An example of using this feature may be:
ClearErrors
${myArray->Read} $R0 1
IfErrors 0 +2
MessageBox MB_OK|MB_ICONEXCLAMATION \
"Could not read from myArray!"
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\ArrayIfErrors.nsi.
1.9.2 Error messages and codes
Error codes are placed in the $ArrayErr after a plug-in function call which you can check yourself with DetailPrint or MessageBox. For a list of error codes and the error messages that they refer to, see plug-in section 2.8.3 Error messages.
Sometimes compiler errors can occur. Those that relate to NSISArray are listed in the section below...
1.9.3 NSIS compiler errors
'Invalid command: ${myArray->Init}'
You must declare at least one function for an array (with ${ArrayFunc}) before using the Init function.
'Invalid command: ${myArray->FuncName}'
You're trying to call ${myArray->FuncName} but you haven't declared it for that array with ${ArrayFunc} first.
'!insertmacro: macro "Array_FuncName" requires [X] parameter(s), passed [y]!'
You're calling ${myArray->FuncName} with too many or too little parameters required by the macro.
'NSISArray: Please declare an array before declaring functions.'
You're trying to use ${ArrayFunc} before declaring an array with ${Array}.
'NSISArray: You cannot declare a function more than once.'
You're trying to declare the same function with ${ArrayFunc} more than once for the same array.
'NSISArray: You do not need to declare the Init and Delete functions.'
The Init and Delete array functions need not be declared with ${ArrayFunc}.
'NSISArray: An invalid function name has been declared.'
You've passed an incorrect array function name to the ${ArrayFunc} function. Check your spelling.
'NSISArray: You can only set the array object style once.'
You can only change the object delimiter once for an array object.
'NSISArray: You cannot declare more than one array with the same name.'
You've already declared an array of the same name with ${Array}.
'NSISArray: An array can only be initialised once.'
You're calling ${myArray->Init} more than once (for myArray).
'NSISArray: The minimum index count is 1.'
The first parameter for ${myArray->Init} or ${myArray->ReDim} must be greater than or equal to 1.
'NSISArray: The minimum buffer length is 2.'
The second parameter for ${myArray->Init} or ${myArray->ReDim} must be greater than or equal to 2. This is because the null escaping character that ends a string must be taken into account.
'NSISArray: You must add at least 8 index reallocation.'
The first parameter for ${myArray->SetAutoReDim} must be greater than or equal to 8.
'NSISArray: You must add at least 8 bytes for buffer reallocation.'
The second parameter for ${myArray->SetAutoReDim} must be greater than or equal to 8.
1.9.4 Enabling error messages with ${ArrayErrorStyle}
By default just the $ArrayErr variable will contain the error code when an array function call fails. However, we can use the following function to enable more debugging features:
${ArrayErrorStyle} [MsgBox|LogWin|Off]
With MsgBox, an error message box will be displayed. With LogWin, the error messages will appear on the NSIS InstFiles Page log window. The error messages will display the caller function name, the error code and the error message that is associated with it.
Use Off to disable the extra error reporting feature.
This instruction can only be used inside Functions and Sections. Using LogWin will only work in Sections.
For a compilable NSIS script example, see Examples\NSISArray\ArrayErrorStyle.nsi.
1.9.5 Special array debugging functions
1.9.5.1 ${myArray->Debug}
This will display a debug screen with a list-box containing the array items in myArray, including some general statistics.
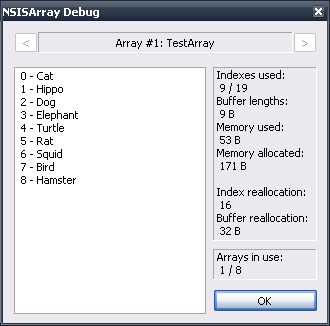
There are also buttons to navigate between arrays that are currently in use.
1.9.5.2 ${myArray->Print} [index]
This will print the value of the item at [index] in the InstFiles page log window (uses DetailPrint). Obviously you need to call this from within a Section (or a Function being called from a Section).
Section "-dummy"
${myArray->Write} 0 "hello"
${myArray->Print} 0 ## Outputs "hello"
SectionEnd
1.10 Examples
1.10.1 Example 1
Name "NSISArray-Example1"
OutFile "NSISArray-Example1.exe"
!include "NSISArray.nsh"
${Array} Array1 5 11
${ArrayFunc} WriteList
${ArrayFunc} Cut
${ArrayFunc} Swap
${ArrayFunc} Concat
Section
## Initialise array for use
${Array1->Init}
## Write a new array
${Array1->WriteList} '"Hi" "I am" "Afrow UK." "My name is" "Stuart!"'
## Cut out 2nd item
${Array1->Cut} $R0 1
DetailPrint $R0 ; == "I am"
## Swap "Afrow UK!" and "Stuart!"
${Array1->Swap} 1 3
## Join strings together with " "
${Array1->Concat} $R0 " "
DetailPrint $R0 ; == "Hi Stuart! My name is Afrow UK."
## Don't need the array anymore
${Array1->Delete}
SectionEnd
1.10.2 Example 2
Name "NSISArray-Example2"
OutFile "NSISArray-Example2.exe"
!include "NSISArray.nsh"
${Array} Array2 5 26
${ArrayFunc} Shift
${ArrayFunc} Push
${ArrayFunc} Write
${ArrayFunc} Sort
${ArrayFunc} Splice
${ArrayFunc} Read
${ArrayFunc} Unshift
Section
## Initialise array for use
${Array2->Init}
## Write a new array
${Array2->Shift} "1st shift"
${Array2->Shift} "2nd shift"
${Array2->Push} "1 push"
${Array2->Push} "2nd push"
${Array2->Write} 4 "I like writing"
## Sort the array alphabetically or numerically
${Array2->Sort} ""
## Replace last two items with one
${Array2->Splice} 3 4 '"I don$\'t like writing much"'
## Read from the array
${Array2->Read} $R0 0
DetailPrint $R0 ; == "1 push"
${Array2->Read} $R0 1
DetailPrint $R0 ; == "1st shift"
${Array2->Read} $R0 2
DetailPrint $R0 ; == "2nd push"
${Array2->Unshift} $R0
DetailPrint $R0 ; == "I don't like writing much"
## Don't need the array anymore
${Array2->Delete}
SectionEnd
1.10.3 More working examples
You can find more working NSIS script examples in the NSIS\Examples\NSISArray folder. There's an example script for every NSISArray script header function.
1.11 Jumping over NSISArray functions
You cannot jump over any NSISArray script header instructions with relative jumps...
StrCmp $R0 "blah" 0 +2
${myArray->Cut} $R1 3
NSISArray script header instructions are macros that contain more than one line of NSIS code and therefore a relative jump will not work. You must use labels to jump to instead...
StrCmp $R0 "blah" 0 noCut
${myArray->Cut} $R1 3
noCut:
1.12 Calculating memory usage
To calculate the amount of memory being used by the NSISArray plug-in, you can use the SizeOf function to return the number of item indices allocated, indices used and the length of allocated buffers. Times them together to get the total number of bytes allocated for use.
${myArray1->SizeOf} $R3 $R1 $R2
IntOp $R0 $R1 * $R2
${myArray2->SizeOf} $R4 $R2 $R3
IntOp $R1 $R2 * $R3
IntOp $R0 $R0 + $R1
## $R0 == total number of bytes allocated by myArray1 and myArray2.
IntOp $R0 $R0 / 1024
## $R0 == total number of kilobytes (KB) allocated by myArray1 and myArray2.
IntOp $R0 $R0 / 1024
## $R0 == total number of megabytes (MB) allocated by myArray1 and myArray2.